Pain Point 3 – Difficulty Identifying Who’s Covering What
Organizations often struggle to clearly determine which external standards, customer requirements, and internal policies apply to each process. Standards such as ISO 9001 contain numerous clauses, and without a structured method to assess applicability, teams are left interpreting requirements inconsistently or relying on institutional knowledge.
Why this matters
When applicability is unclear, organizations either miss required controls or invest time and resources addressing requirements that do not apply. This creates compliance gaps, unnecessary complexity, and confusion across teams. During audits, these gaps surface as unclear scope, inconsistent implementation, or missing evidence. From a business perspective, the result is wasted effort, delayed certifications, increased audit findings, and frustration among process owners who are unsure of expectations.
The better way
A clear, structured method for determining and documenting applicability. By systematically mapping requirements to processes, organizations can:
Clearly define which clauses apply and why
Identify gaps before audits occur
Align process owners around shared expectations
Maintain consistency as standards, processes, or scope change
With this approach, compliance becomes deliberate and efficient rather than reactive.
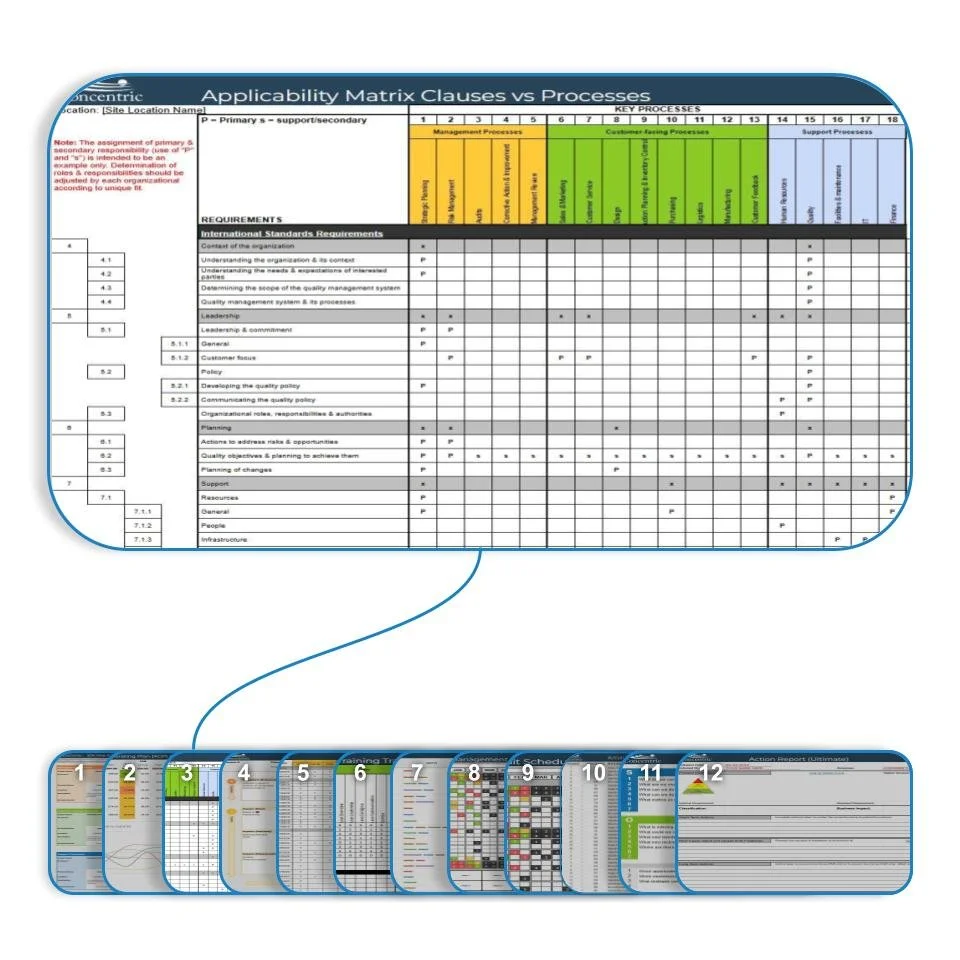
Tool 3: Applicability Matrices
The Applicability Matrices provide a structured, scalable way to map external and internal requirements directly to organizational processes. Using a clear, grid-based format, the tool documents which clauses apply, where they are addressed, and where gaps exist—creating immediate visibility and traceability.
Built in a flexible, spreadsheet-based environment, the tool supports customization across multiple standards (such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or customer-specific requirements). It enables easy updates, filtering, and export for audits, while linking seamlessly to process maps, risk assessments, and corrective actions. Refined through more than 30 years of real-world application, it ensures comprehensive coverage without unnecessary complexity.
This tool removes guesswork and replaces it with clarity.
How Tool 3 Fits into the 12 Tools™ System
The Applicability Matrices connect organizational intent to operational reality. Building on the system scope defined in Tool 1 and supporting the process clarity established in Tool 4, this tool ensures that every applicable requirement is clearly understood, owned, and addressed. It forms the backbone of audit readiness, risk identification, and corrective action.
Apply the matrix to a new or existing standard, validate it with process owners, and keep it current as your system evolves. Practitioner feedback continues to shape how this tool is refined and improved.
Other Commonly Used Tools (and Their Limitations)
MasterControl
A quality management platform with automated compliance matrices and audit traceability.
Strength: Strong requirement linking and reporting.
Limitation: Higher cost and broader system overhead.ETQ Reliance
A configurable quality and risk management platform.
Strength: Flexible matrix and analytics capabilities.
Limitation: Initial setup and configuration effort required.Qualio
An electronic QMS focused on requirement traceability and collaboration.
Strength: User-friendly interface and collaboration features.
Limitation: More heavily oriented toward regulated industries.Intelex
An EHSQ platform with dashboards for applicability mapping and gap analysis.
Strength: Cloud-based scalability across disciplines.
Limitation: Broader scope beyond quality and compliance may add complexity.